Solar panel technology is becoming increasingly popular, and more and more households are choosing to install solar panels. This not only improves household energy independence, but also utilizes renewable energy to save utility costs.
So, how does rooftop solar panels work to benefit thousands of households? This article will take you to understand the working principle of solar panels together.
Solar panel technology relies on photovoltaic (PV) cells that use silicon as a semiconductor and insulator. The battery is relatively small and can generally generate 1-2 watts of electricity. Photovoltaic cells are connected into chains, forming modules or panels to increase power generation.
These modules can be used alone or combined into an array. The photovoltaic cells are sandwiched between glass and/or plastic protective materials to prevent wind and rain erosion, and the solar panels also use anti reflective coatings to increase their absorption of sunlight.
You may have experienced the heat emitted by road surfaces on hot days, because when sunlight shines on asphalt pavement, the heat of the sun causes molecules on the pavement to move faster and become hotter. When using solar panels, sunlight does not heat them up. On the contrary, solar cells absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity.
So, how do solar panels work on houses? The photovoltaic modules and arrays are installed on the sunny side, allowing the solar panels to receive sunlight most effectively even on cloudy days.
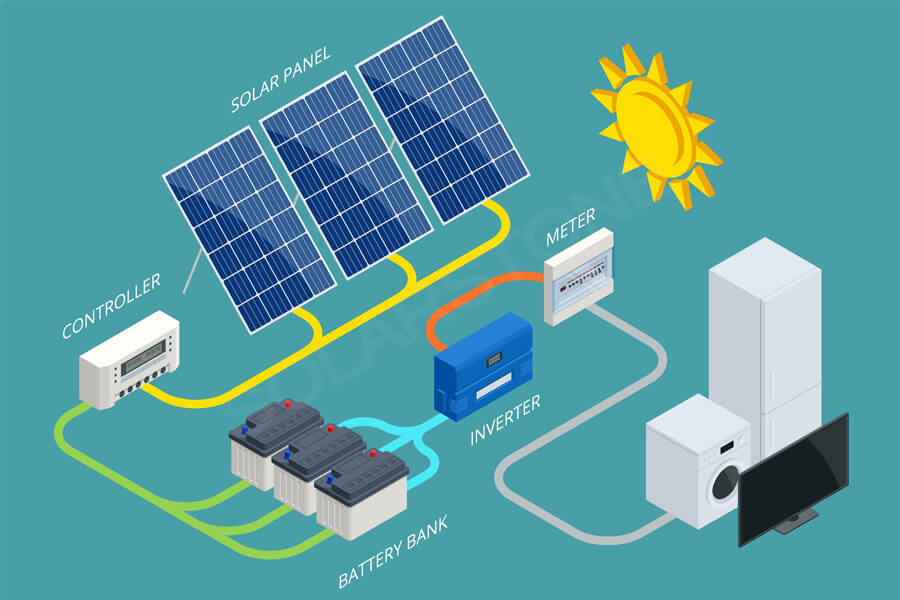
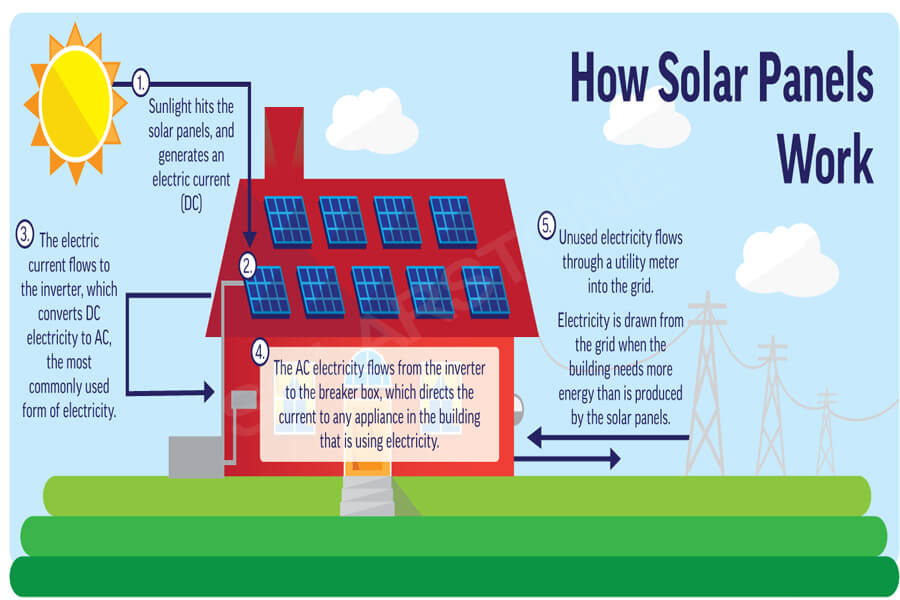
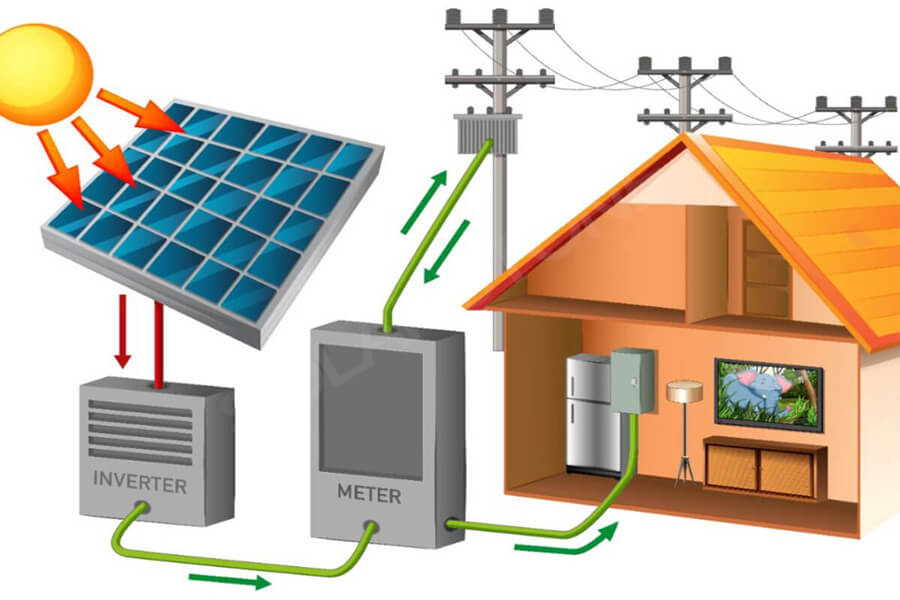
The photovoltaic cells in the solar panel array absorb energy from sunlight, and the metal plates next to the solar cells collect the generated DC electrons and transmit the electricity to the connecting wires. Solar inverters convert electricity into alternating current to power household appliances.
If the household solar cell array is connected to the power grid, the excess electricity generated by the solar panels can be sold back to the grid, further reducing the electricity cost for users. If the user has a household battery energy storage device, it can be integrated to store excess electricity and create a microgrid.
Environmental and economic benefits of household solar panels
Solar energy is a renewable and clean energy source that can reduce people’s dependence on non renewable resources. Solar energy helps to reduce carbon footprint, improve electrical efficiency, and accelerate the transformation of electric vehicles, thereby protecting the environment.
Solar energy integration technology enables homeowners and multi household buildings to generate electricity on their own, reducing their dependence on traditional power grids and providing power during power outages. Meanwhile, solar energy can also bring economic benefits to households.
Solar panels can significantly reduce household water and electricity costs, and the specific cost savings may vary depending on the electricity price and solar array size, as well as regional location, energy usage, solar cell system size, and local electricity prices.
However, solar panels can save households an average of $1000 to $1500 per year. According to reports, most households have saved $20000 to $96000 in water and electricity costs during the lifespan of solar panels, greatly reducing their economic burden.
If the home solar system is connected to the grid, residents can output excess electricity back to the grid. This process is called “net metering”, which allows residents with solar or other renewable energy to produce clean electricity and distribute it to other residents in the region, further reducing utility bills.
In the past decade, the installation cost of solar energy systems has decreased by more than 50%. The average investment payback period for installing solar cell arrays is ten years, while solar panels have a lifespan of up to 25 years and require almost no maintenance, which means residents will save decades of electricity bills.