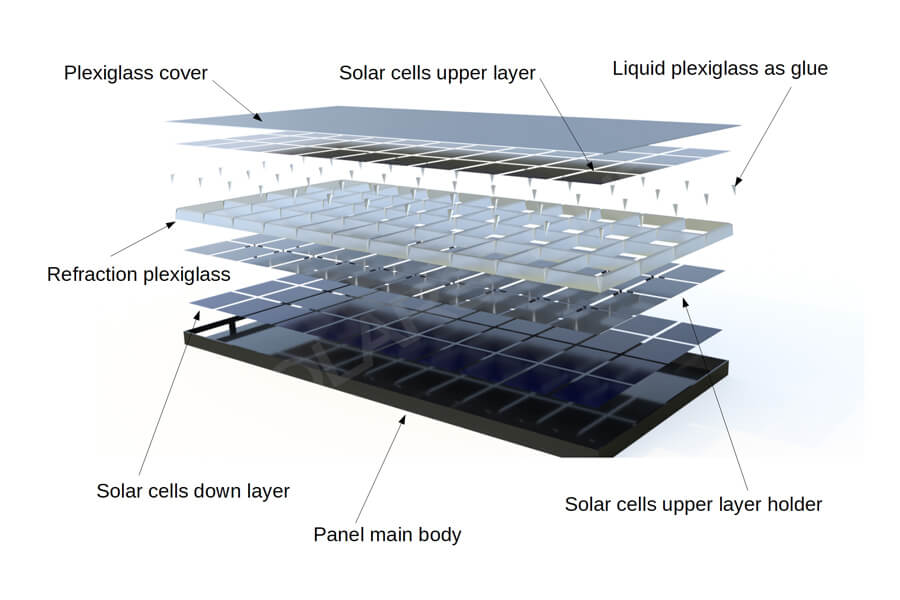
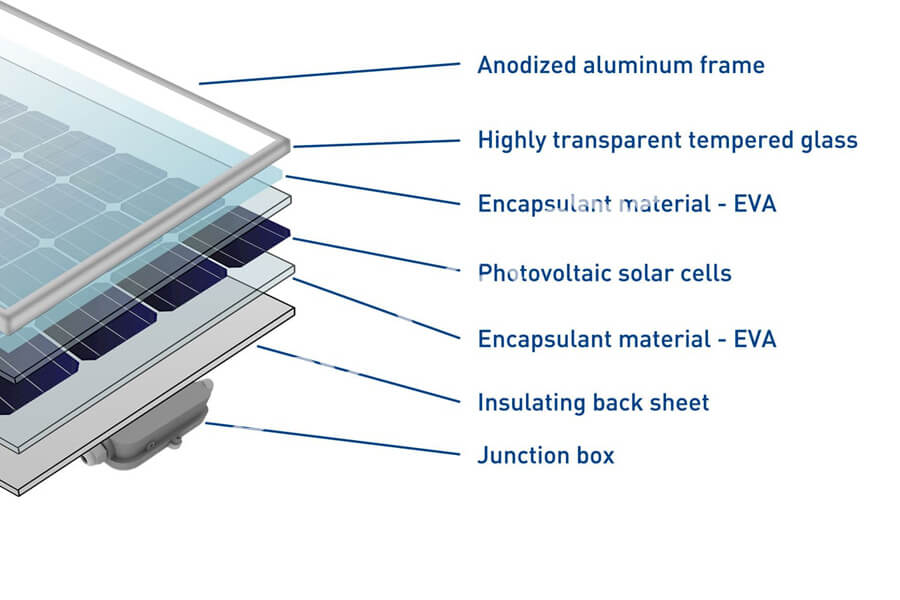
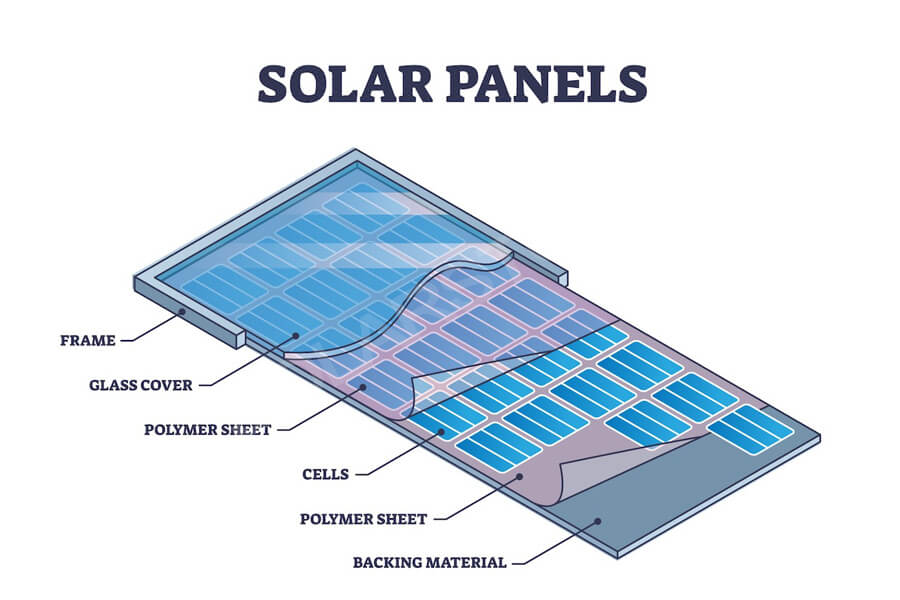
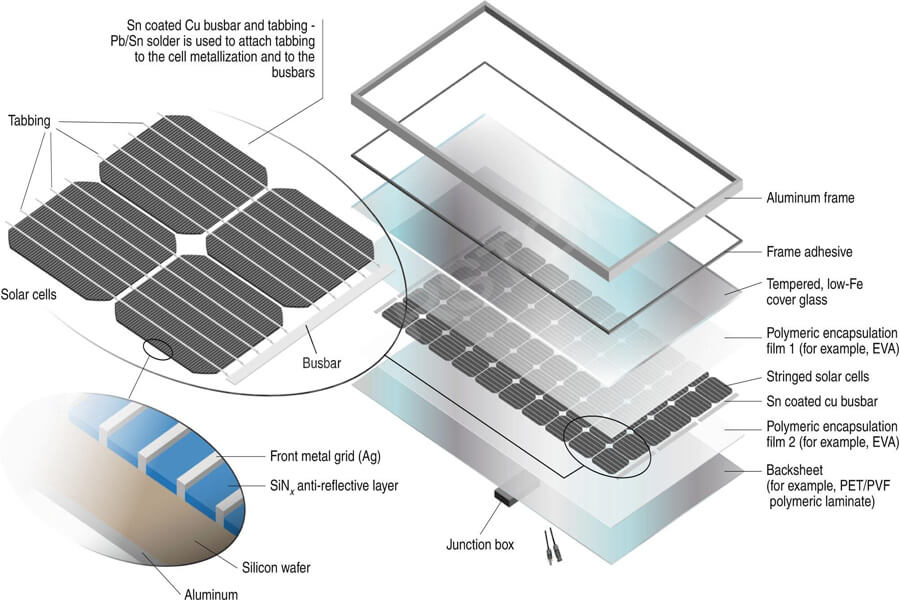
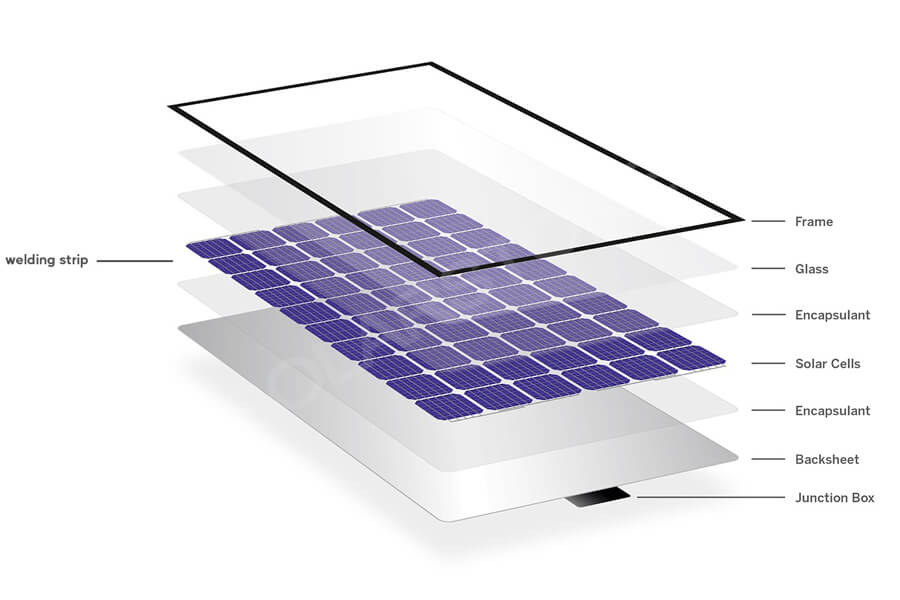
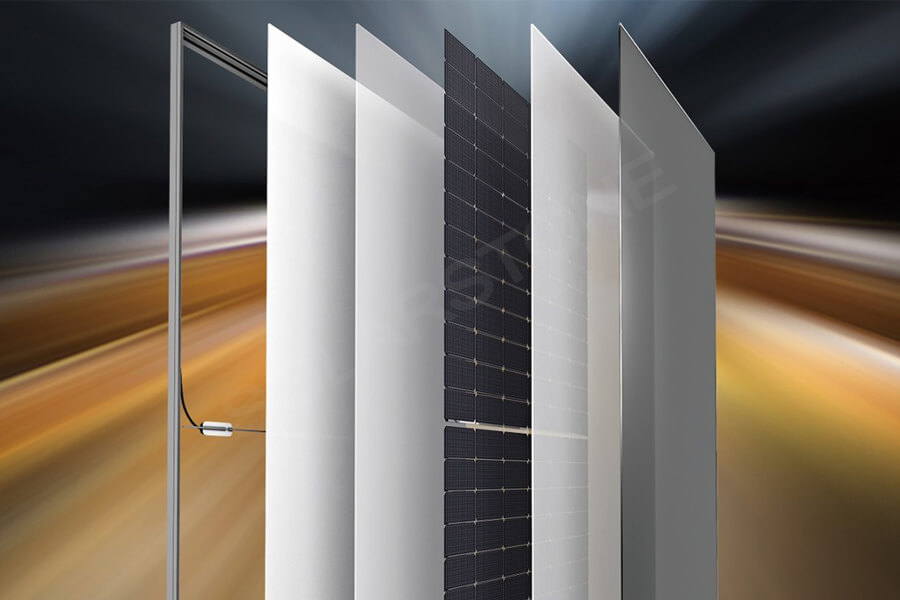
Photovoltaic modules refer to the smallest photovoltaic cell assembly and combination device with packaging and internal connections, which can provide direct current separately and cannot be separated. It is the core component of a photovoltaic power generation system, composed of eight core materials.
01. Solar cells
Solar cells are the core components of a module, mainly used to convert light energy into electrical energy. After the solar cells are connected in series or parallel to reach a certain rated output power and voltage, they form photovoltaic modules.
The photovoltaic modules are combined to form a photovoltaic array, which is connected to components such as controllers, battery packs, inverters, etc. to form a photovoltaic power generation system.
Solar cells are divided into monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, and amorphous silicon solar cells based on their raw materials. Crystal silicon battery technology is based on silicon wafers as the substrate, and generates electricity by separating photo generated carriers according to the PN junction.
According to the differences in raw materials and battery preparation technology, crystalline silicon batteries are divided into P-type batteries and N-type batteries.
P-type silicon wafers are made by doping boron elements into silicon materials. The preparation techniques for P-type batteries include traditional AL-BSF (aluminum back field) and PERC technologies;
N-type silicon wafers are made by doping phosphorus elements into silicon materials. There are many techniques for preparing N-type batteries, including PERC, TOPCon, IBC, and HJT.
02. Glass
Photovoltaic glass is a type of sodium calcium silicate hydrochloric acid glass mainly used for packaging photovoltaic modules. Photovoltaic glass directly affects the power generation efficiency and service life of photovoltaic modules.
Photovoltaic glass is generally low iron tempered glass or semi tempered glass, which has the following characteristics. One is good permeability. The transmittance is a key factor affecting the conversion efficiency of photovoltaic cells. Photovoltaic glass needs to have high transparency and high reflectivity towards 1200nm infrared light. The second is high mechanical strength.
Impact resistant, capable of withstanding 2400Pa wind pressure and 5400Pa snow pressure, providing support and protection. Thirdly, it has good durability.
Due to the influence of climate and geographical location, components need to operate in outdoor environments with large temperature differences between day and night, and must have characteristics of corrosion resistance and weather resistance.
03. Adhesive film
Photovoltaic packaging film is an important component of photovoltaic modules, located on the upper and lower sides of solar cells. The primary function of the adhesive film is to bond the battery with the glass and back panel.
Secondly, the adhesive film can play a protective role in packaging, protecting the battery circuit from external environmental interference and extending the service life of the components.
In addition, the encapsulation film can enhance the transparency of photovoltaic modules, thereby improving the power generation efficiency of the modules. Finally, the adhesive film can also serve as a structural support and positioning for the battery during component production, storage, installation, and use.
According to the materials, the mainstream adhesive films mainly include EVA, POE, EPE, and PVB. EVA film is the mainstream photovoltaic packaging film, which has good transparency, good processing performance, stable supply, and low cost.
However, it has disadvantages such as high water vapor penetration, low impact resistance, and unstable PID resistance. POE film has low water vapor transmittance and good PID resistance, making it suitable for packaging double glass and N-type components. However, it has poor processing properties and high cost.
04. Backboard
Photovoltaic backboards are packaging materials used for back protection and are generally used for single glass modules. Photovoltaic backboards are divided into fluorinated backboards and non fluorinated backboards. Fluorinated backboards include TPT, TPE, TPC, CPC, while non fluorinated backboards include PET, PA/PO, etc.
Photovoltaic backboards are mainly used to resist the erosion of solar cells, adhesive films, and other materials in humid and hot environments. They play a role in corrosion resistance, weather resistance, oxidation resistance, and insulation protection, and can effectively extend the service life of modules.
The white back panel has a high reflectivity, which can improve the conversion efficiency of the components. Meanwhile, the high infrared reflectivity also facilitates the reduction of the operating temperature of the components.
05. Border
The photovoltaic frame is a frame installed on the outer side of the glass, mainly used to fix and seal solar cell modules, facilitating the transportation and installation of photovoltaic modules. The installation of the frame is beneficial for protecting the glass edges and enhancing the sealing performance of photovoltaic modules.
At the same time, the frame is the connecting carrier between the load-bearing component and the bracket. The use of the frame can improve the overall mechanical strength and load resistance of the component, thereby extending its lifespan.
06. Welding strip
Photovoltaic solder strips are composite conductive materials formed by coating tin based solder on the surface of copper strips. They are used in series or parallel connection of solar cells to collect current and conduct electricity. They are important materials in the welding process of photovoltaic modules.
Photovoltaic solder strips are divided into interconnect solder strips and busbar solder strips. Interconnecting solder strips are used to connect solar cells, collect and transmit solar cell current.
The busbar is used to collect the current generated by the solar cell string and lead it out to the junction box. Welding strips have a direct impact on current collection, which in turn affects the power and power generation efficiency of components.
In the early days of the industry, flat welding strips were used. With the development of the industry, currently, high-efficiency components all use round welding strips.
07. Silicone
Silicone is mainly used for bonding and sealing laminated glass photovoltaic modules, bonding frames to glass, junction boxes to backboards (or glass), and playing a sealing and connecting role.
According to the different usage locations, silicone is divided into sealant and potting adhesive. Sealant is used inside the frame card slot and at the bottom of the junction box and backboard. Sealing glue is generally used inside the junction box to protect the internal circuits.
08. Junction box
The junction box mainly consists of a junction box cover, sealing ring, diode, heat dissipation device, box body, wires, and connectors. The main function of a junction box is to connect the electricity generated by solar cells to external circuits.
It can seal, waterproof, and dustproof the outgoing lines of photovoltaic modules. The junction box also serves to protect the safe operation of the photovoltaic module system. If a module experiences a short circuit, the junction box will automatically disconnect the short circuit solar cell string to prevent the entire system from being burned out.