1. Test conditions of solar cell array
Since the output power of the solar cell module depends on the solar irradiance, the distribution of the solar spectrum and the temperature of the solar cell, the measurement of the solar cell module shall be carried out under standard conditions (STC).
The measurement conditions are defined as Standard No. 101 by the European Commission, and the surface temperature of the solar cell panel is set at 25 ℃, The test under the condition that the solar radiation intensity is 1000W / ㎡ is called the standard test state.
Under this condition, the maximum power output by the solar cell module is called the peak power, expressed as WP (peak watt). In many cases, the peak power of components is usually measured by solar simulator and compared with the standardized solar cells of international certification bodies.
It is difficult to measure the peak power of solar cell modules outdoors, because the actual spectrum of sunlight received by solar cell modules depends on atmospheric conditions and the position of the sun;
In addition, in the process of measurement, the temperature of solar cells is also changing, so the error of outdoor measurement of solar cell modules can easily reach 10% or more. Test conditions for measuring solar cell modules outdoors:
1) The weather is fine, there is no cloud around the sun, and the total solar irradiance is not less than 700MW / cm2.
2) The irradiation instability in the test cycle shall not be greater than ± 1%. The calculation of irradiation instability shall be in accordance with the relevant provisions of the test method for electrical performance of ground solar cells, and the surface of the tested array shall be clean.
The technical parameter test and requirements of solar cell module are as follows:
1) The electrical performance parameters of solar cell array shall be tested according to the relevant provisions of test method for electrical performance of ground solar cells and measurement method for parameters of solar cell modules (ground).
2) The open-circuit voltage of solar cell array shall meet the design requirements.
3) The measured maximum output power of solar cell array shall not be less than 90% of the total maximum output power of each module.
4) The insulation resistance between the output end of the solar cell array and the support structure shall not be less than 50m Ω.
After the solar cell array is tested, the junction box covers of all solar cell modules shall be covered and locked, and obvious polarity marks and number marks of sub-arrays shall be marked on the output end of the solar cell array.
2. Main technical parameters of solar cell module
The main technical parameters of solar cell modules are:
1) Photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar cell module η%. The photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar cell module refers to the ratio of solar cell module to convert received light energy into electric energy:
η= P0/E × 100%
Where: η Conversion efficiency; P0 is the output power; E is the solar energy irradiated by the solar cell module.
The conversion efficiency of solar cell modules is an important index to evaluate the performance of solar cell modules and an important factor to determine whether solar cell modules have use-value.
The theoretical conversion efficiency limit of crystalline silicon solar cells is 29%, and solar cells still have a lot of room for development in technology.
2) The voltage V of a single solar cell is 0.4V ~ 0.6V, which is determined by the physical properties of the material.
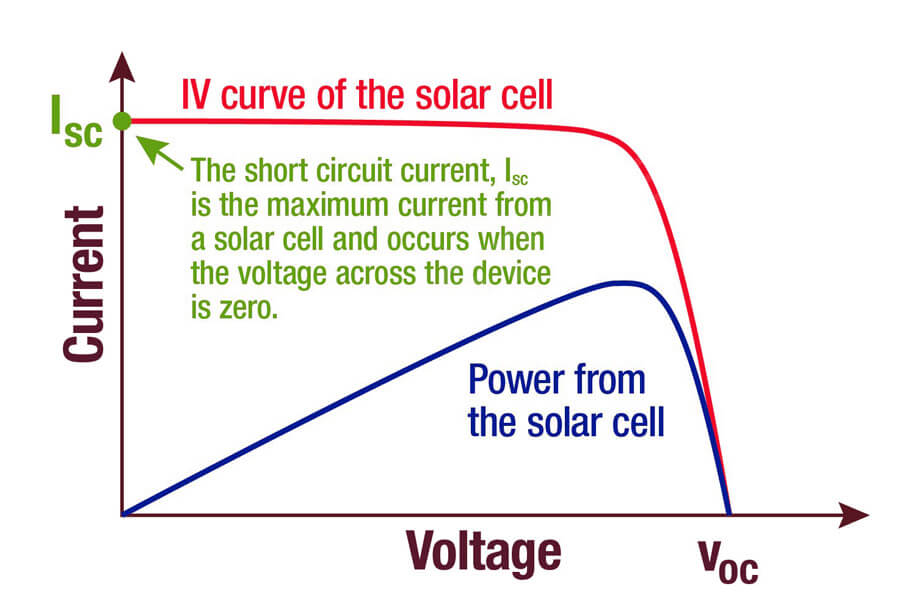
3) The filling factor FF% is an important index for evaluating the load capacity of solar cells:
FF=(Im × Vm)/(Isc × Voc)
Where ISC is the short-circuit current, VOC is the open-circuit voltage, IM is the optimal working current and VM is the optimal working voltage.
The output power of solar cell module is closely related to its area. The larger the area, the greater the output power under the same lighting conditions. The advantages and disadvantages of solar cell modules are mainly measured by open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current.
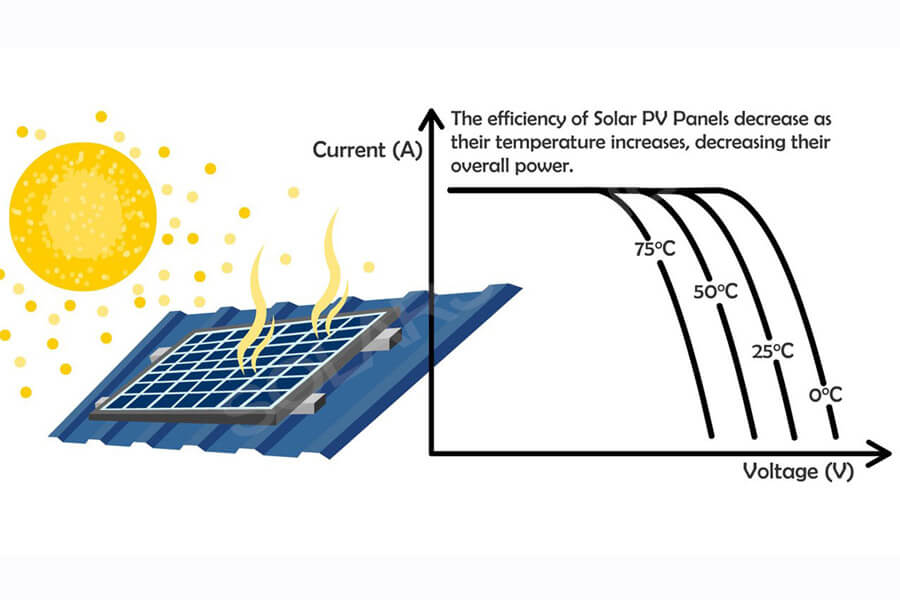
4) The ambient temperature and the temperature of the solar cell module directly affect the performance of the solar cell module. When the temperature increases, the open-circuit voltage decreases in a linear relationship. Solar cell modules of different materials have their own operating temperature range.
For a certain solar cell module, the optimal load required to obtain the maximum output power is also different at different temperatures. For example, under standard conditions: AM1.5 light intensity, t = 25 ℃, the output power of a certain type of solar cell module is 100wp. If the temperature of the solar cell module rises to 45 ℃, the output power will not reach 100wp.