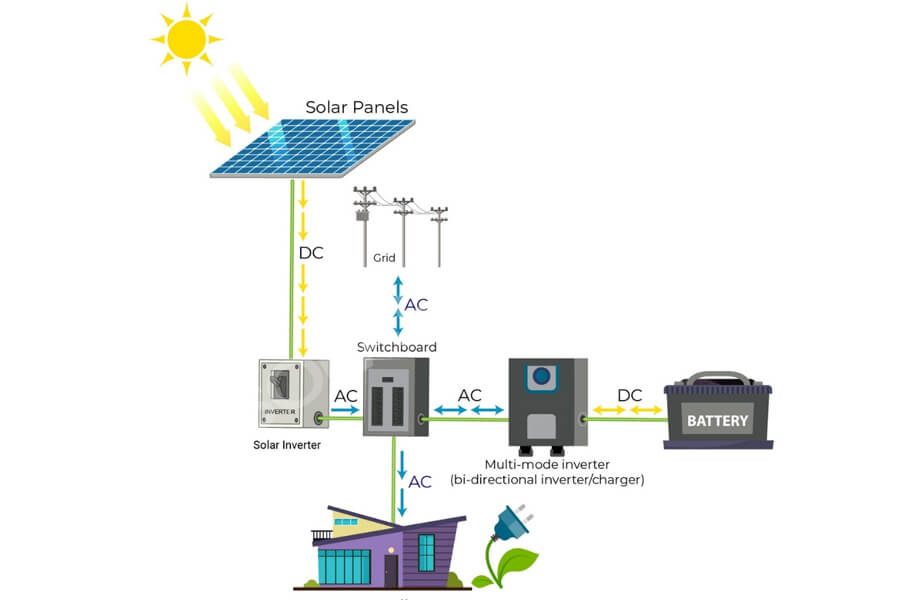
Inverters play a crucial role in the entire photovoltaic system, and their quality determines the efficiency and lifespan of the photovoltaic power generation system, making them the core of the entire power generation system.
Today, let’s learn how to choose the appropriate photovoltaic inverter:
1. Determine the type of photovoltaic inverter
At present, commonly used inverters are roughly divided into centralized inverters, string inverters, and micro inverters. The type to choose depends on the actual application requirements of photovoltaic systems.
2. Understand the main functions of inverters
In the previous article, we have taught everyone the main functions that inverters should have. It generally includes functions such as automatic operation and shutdown, anti islanding effect, maximum power point tracking control, etc.
3. Understand how many MPPT inputs the inverter has
When selecting an inverter, it is important to understand how many MPPT inputs the inverter has; The number of MPPT paths of the inverter basically determines the power generation of a photovoltaic power plant, and is closely related to whether the photovoltaic system is easier to design for distribution boards.
4. Understand the power generation efficiency of inverters
The performance and failure rate of inverter components will affect the power generation efficiency of the inverter, and these factors are also factors that we need to pay attention to when selecting the inverter.
Generally speaking, the higher the upper limit of the inverter’s working voltage range, the stronger the inverter’s ability to withstand power generation during peak periods, and the lower the lower limit of the inverter’s working range, which means that the inverter starts earlier and shuts down later;
5. Determine the power of the photovoltaic inverter
The power required by the inverter can be calculated based on the total power of the solar panel and its average daily/monthly electricity consumption. Generally speaking, the selection of inverter power should be greater than the power of the solar panel.
For example, if the solar panel is 2000W, the power of the supporting inverter should exceed 2000W. If the electrical load involves impulse or inductive loads, the inverter needs to choose a more relaxed power range;
6. Understand the heat dissipation method and overload capacity of the inverter
The heat dissipation method of the inverter also affects the power of the inverter. At present, the common heat dissipation methods for inverters include natural cooling, forced air cooling, water cooling, etc.
These heat dissipation methods, especially water cooling, are mostly applied to large inverters; Generally, regular and high-quality inverters have an overload capacity, with approximately 1.1 times the overload margin reserved.