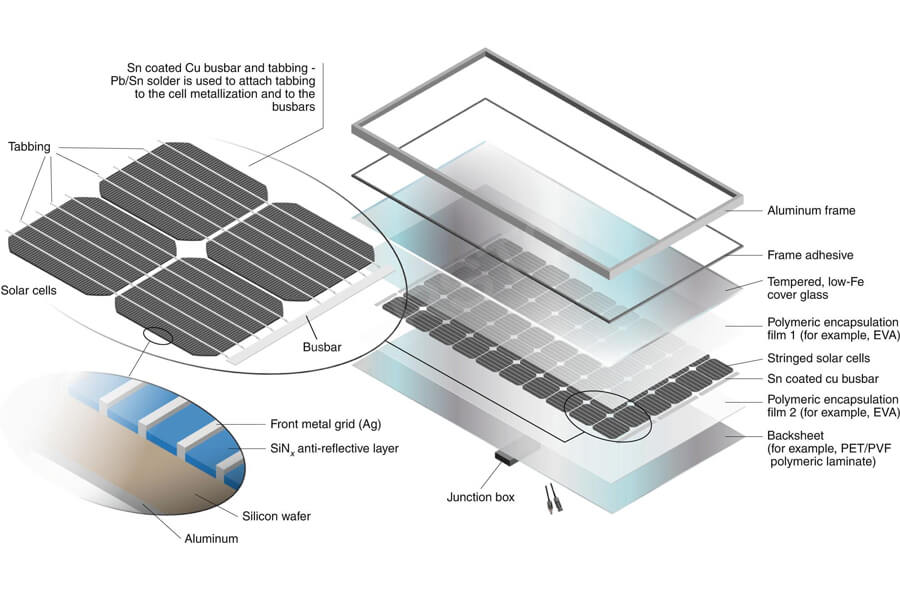
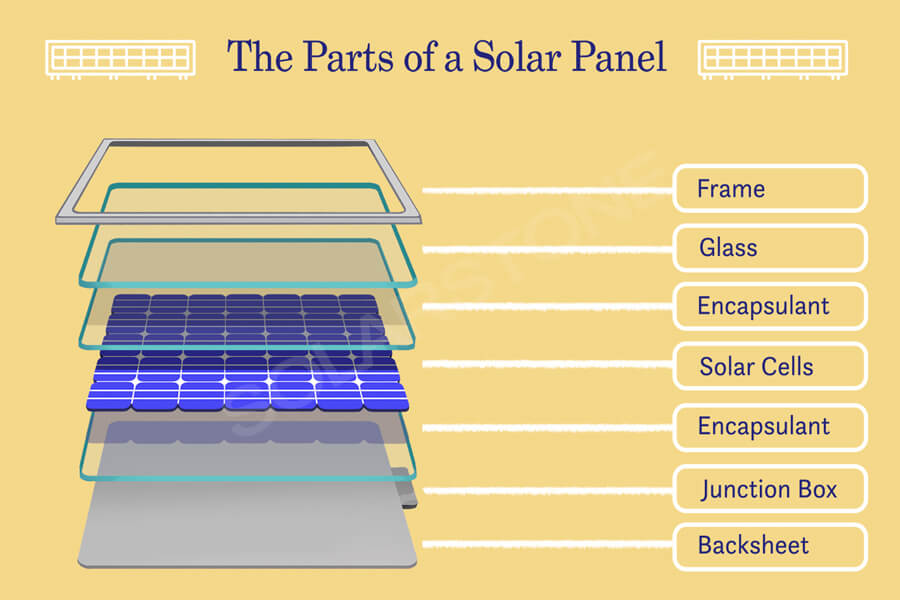
Core component – solar cells
From a functional perspective, solar cells are semiconductor thin films obtained by processing silicon wafers, which can convert solar energy into electrical energy, determining the power generation capacity of photovoltaic systems.
The principle is the photovoltaic effect and PN junction. The conversion efficiency of solar cells directly affects the power generation efficiency of photovoltaic systems, and the excellent production process of solar cells directly affects the service life of photovoltaic systems;
From the perspective of cost proportion, solar cells are the core of the cost of photovoltaic modules, and also the main way to reduce the cost of photovoltaic modules.
Electrical connection devices – solder strips, junction boxes
From a functional perspective, solder strips can be divided into interconnected solder strips used to connect solar cells in series and busbar solder strips used to connect battery strings and junction boxes.
They are used to collect the converted current of solar cells and are the core electrical connection components in the module, directly affecting the collection efficiency of module current and the fragmentation rate of solar cells.
The junction box can transmit the current generated inside the component to the external circuit. The performance of the diode in its structure is to form a bypass path to maintain normal operation in the event of component failure (bypass diode), and to prevent current backflow (blocking diode) in low light conditions;
From the perspective of cost proportion, the ribbon welding process often adopts a pricing model of “raw materials+processing fees”, and the price is subject to significant fluctuations in the prices of raw materials such as copper and tin.
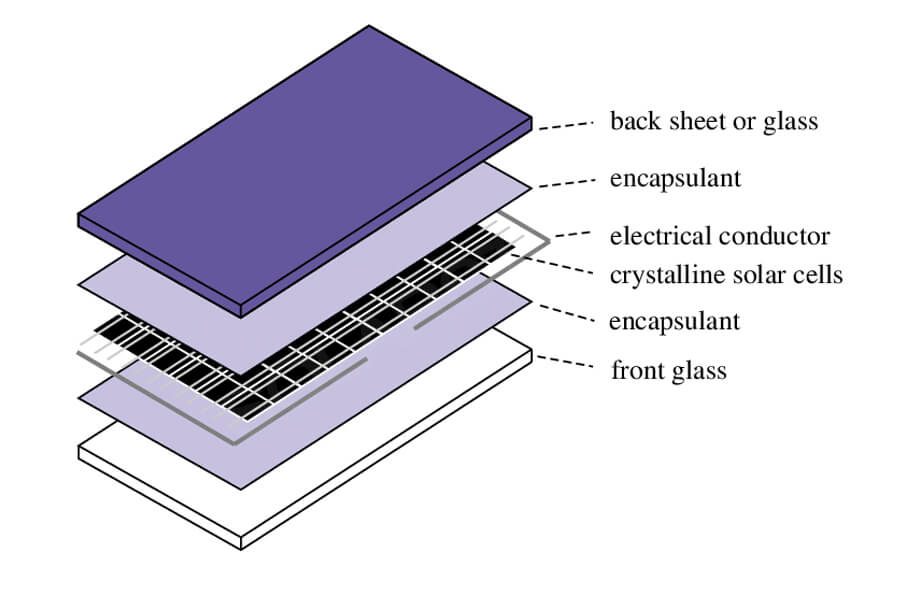
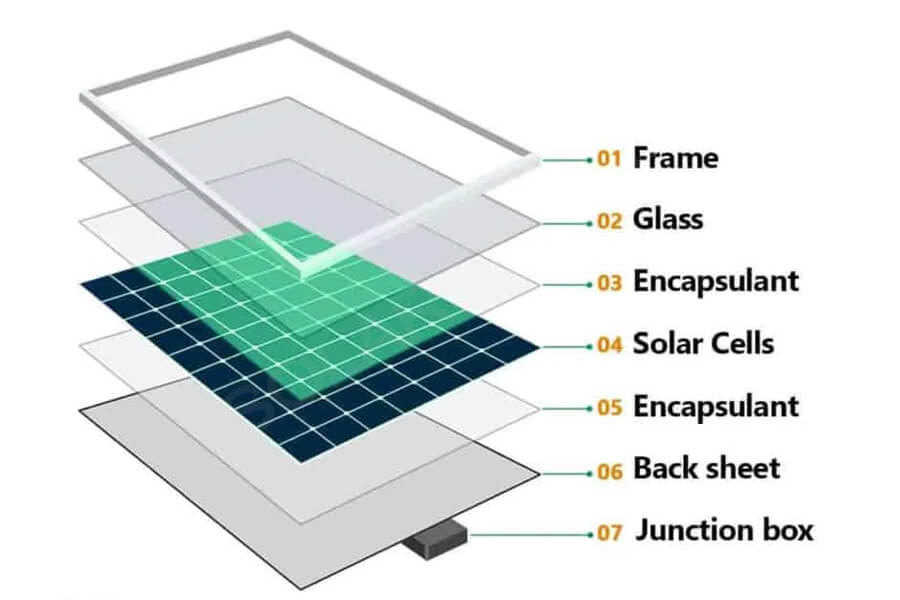
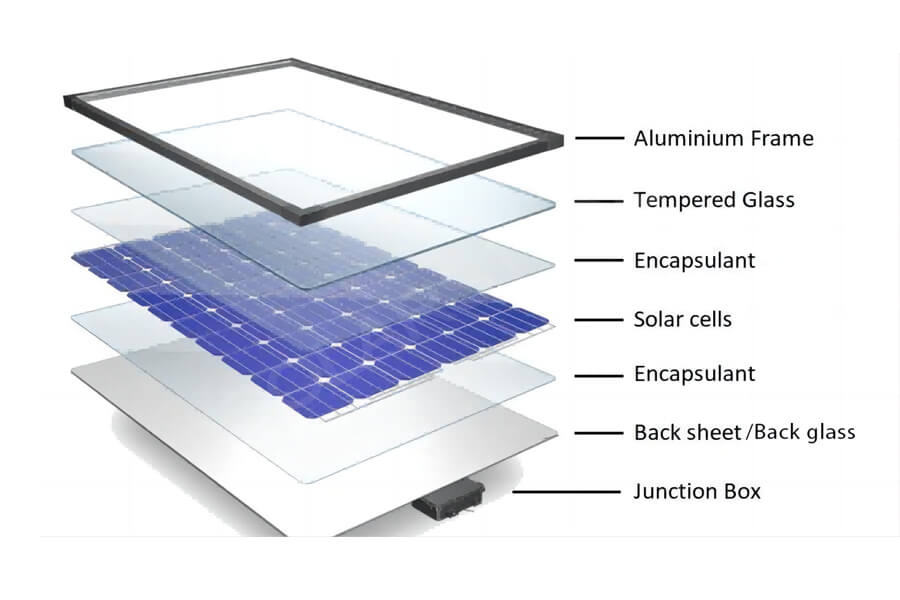
Packaging materials – photovoltaic glass, backboard
From a functional perspective, photovoltaic glass is a special type of glass that can utilize solar radiation to generate electricity and draw current. It is also the outermost transparent packaging panel of the module, mainly serving as a transparent and protective panel.
Compared with traditional glass, it has advantages such as low iron content, high light transmittance, high temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. Its quality directly affects the power generation efficiency and service life of the module.
Backboard is the packaging material for the back of the component, mainly composed of organic polymer materials, as well as inorganic materials suitable for double crystal silicon components (such as glass backboard).
Backboards can protect photovoltaic modules from external environmental erosion such as light, humidity, and heat. Backboards with high light reflectivity can also improve the overall photovoltaic conversion efficiency of the modules.
Packaging auxiliary materials – EVA film, aluminum frame
From a functional perspective, photovoltaic film has superior adhesion, durability, and optical properties, mainly bonding solar cells with glass and backplates, playing a role in protecting solar cells and isolating air.
Due to the irreversible bonding process, the quality of the adhesive film directly determines the packaging quality and service life of the component. Aluminum frame, as the outermost packaging structure of the component, has stronger load-bearing capacity and corrosion resistance compared to steel frame and rubber clip short frame.
At the same time, it is lightweight and perfectly meets the characteristics and requirements of the component. It is an irreplaceable rigid auxiliary material in the short to medium term.