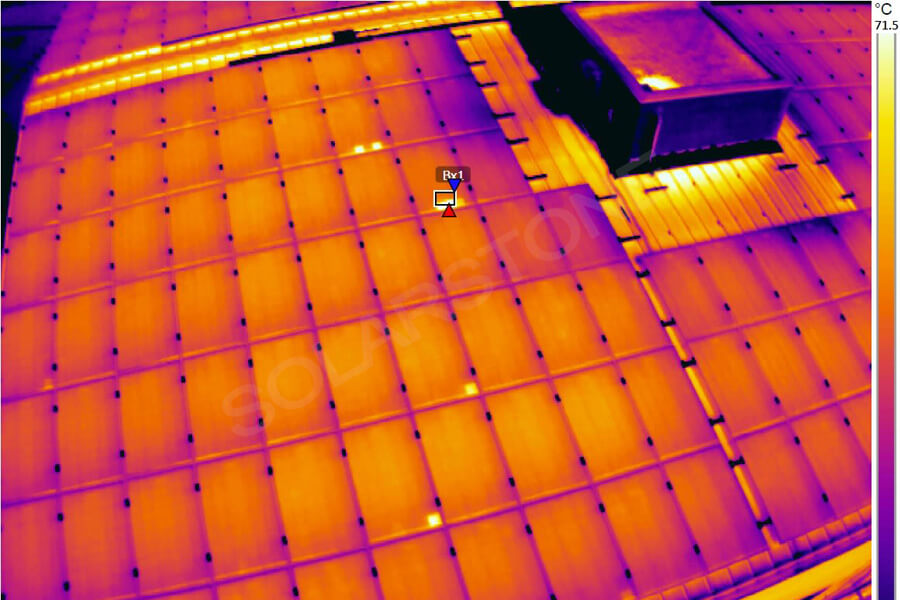
Due to the fact that solar cell modules are usually installed in wide and sunny areas, they are inevitably obstructed by various obstacles during long-term use.
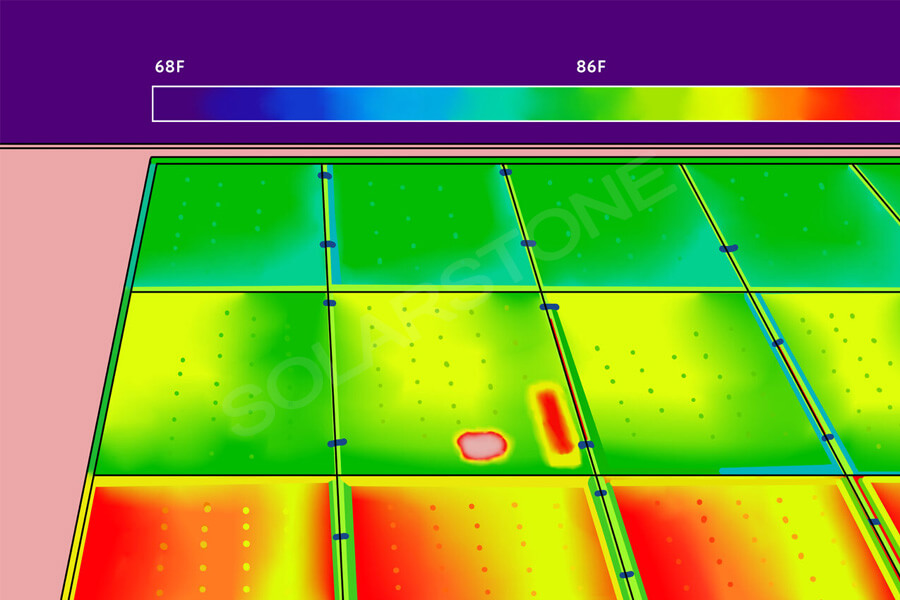
Given the presence of these obstructions, they can create shadows on the surface of the solar cells of the photovoltaic module, which not only leads to a decrease in the output power of the photovoltaic module, but may also cause hot spot effects.
What is the hot spot effect
The hot spot effect of photovoltaic modules refers to the phenomenon where, under certain conditions, the obstructed or defective areas in the series branches of photovoltaic modules in power generation are treated as loads, consuming the energy generated by other areas and causing local overheating. This phenomenon is called the “hot spot effect” of photovoltaic modules.
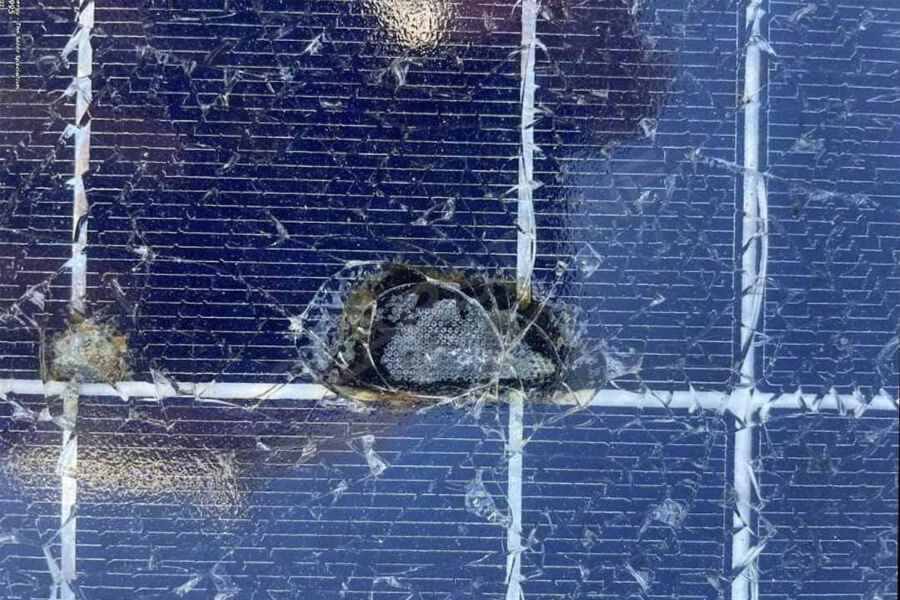
The hot spot effect can reduce the output power of photovoltaic modules to a certain extent. If the heating temperature exceeds a certain limit, it can cause local burning of photovoltaic modules, forming dark spots, melting of solder joints, aging of packaging materials, and other permanent damage. It is an important factor affecting the output power and service life of photovoltaic modules, and may even lead to safety hazards.
The causes of the hot spot effect
There are many reasons that can cause the generation of hot spot effect in photovoltaic modules. When the power of the solar cell is mixed, the grid lines are poorly soldered, or there are defects in the cell itself, such as bubbles, delamination, internal connection failure, etc., the hot spot effect will occur.
Severe cracking or fragmentation of photovoltaic modules can also lead to hot spot effects. Excessive vibration, external impact, or uneven force on the glass surface during transportation and installation of photovoltaic modules can all cause cell cracking.
Cell cracking is also a defect of solar cells. For component paths, an increase in resistance at hidden cracks can easily cause hot spot effects.
The surface of photovoltaic modules is covered by stubborn stains or debris, as well as vegetation and foreign objects. Due to the decrease in electronic transition activity of the solar cells in the obstructed area, the corresponding resistance increases, and the loss also increases.
The loss will be released in the form of temperature, and the increase in temperature in the obstructed area will cause the hot spot effect.