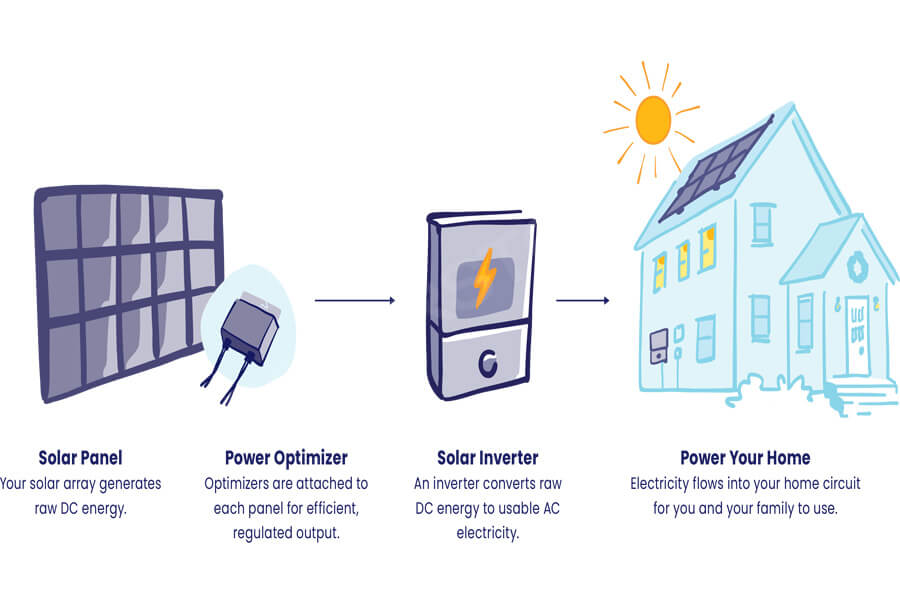
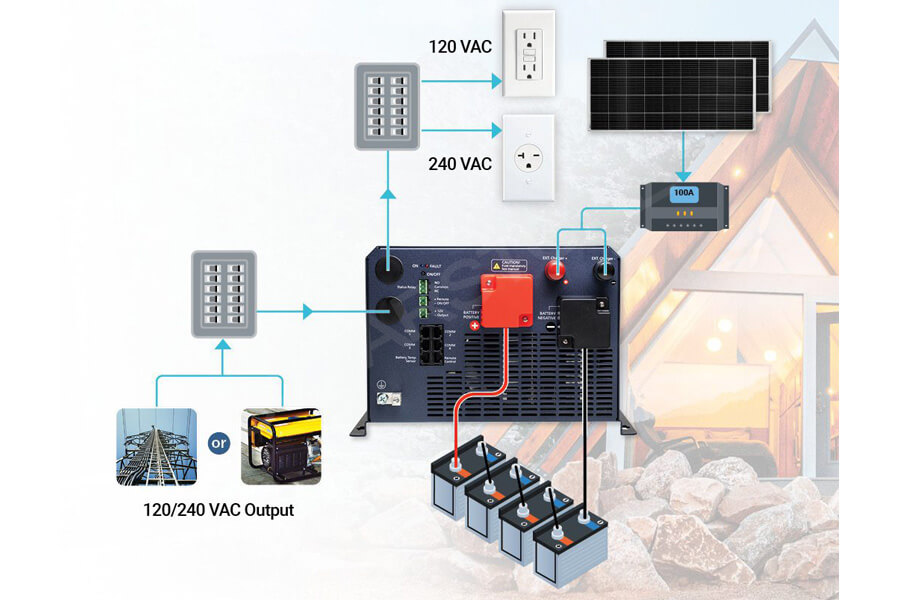
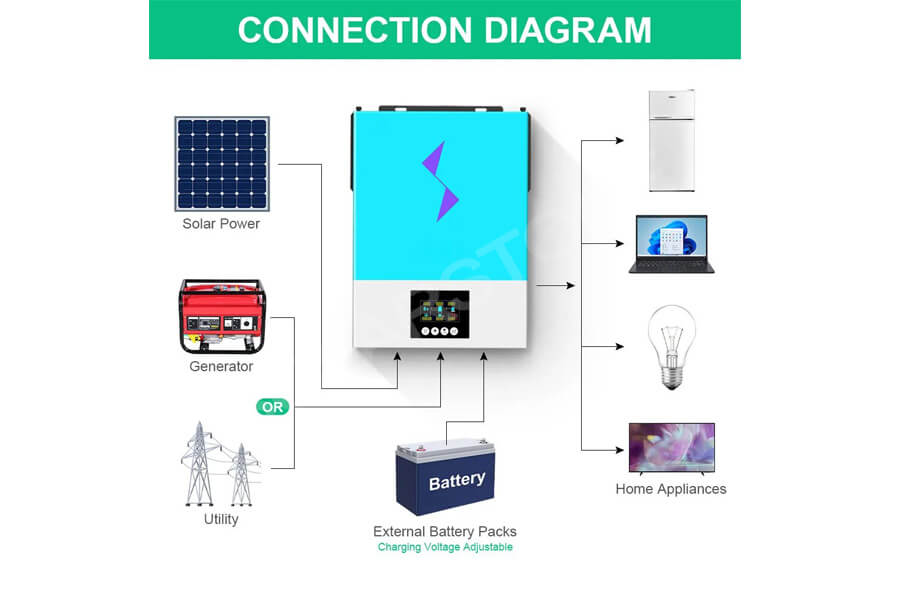
How large does my home need a solar inverter?
There is a common misconception that your solar inverter capacity should match the total wattage of the solar panel, but this is not the case. The capacity of the inverter is lower than its corresponding solar cell array.
- You can only determine the optimal inverter capacity through professional solar design. However, solar systems typically have a DC-AC ratio of 1.25 or higher.
- For example, if a 6kW solar panel system (DC) is connected to a 5kW inverter (AC), the DC-AC ratio is 1.20.
- This value is also known as the inverter load ratio or ILR.
There are technical reasons for using inverter capacity that is lower than the wattage of the photovoltaic array. Considering that solar panels are tested under ideal laboratory conditions, this does not represent the actual conditions for roof installation.
Therefore, solar panels only generate nameplate watts during a small portion of their working time.
If the inverter you install matches the total power of your solar panel, it will operate below the rated capacity in most cases. In other words, you need to pay for additional inverter capacity that has almost never been used. You can use smaller and cheaper inverters to achieve better investment returns and “reduce” the occasional remaining solar peak.
What does MPPT mean in the specifications of solar inverters?
The best solar inverters have a function called MPPT, which represents maximum power point tracking. MPPT is a power optimization method that can increase the power output of solar systems – as their productivity increases, your electricity savings will also be higher. MPPT technology is based on the following principles:
- The sunlight conditions are constantly changing, depending on time and season, and the ideal working voltage and current of solar panels will also change.
- An MPPT circuit continuously adjusts the voltage and current of the photovoltaic array, so solar panels can provide more electricity.
The sunlight conditions also vary depending on the direction of the solar panels. For example, panels facing east receive more sunlight in the morning, while panels facing west receive more sunlight in the afternoon.
When solar panels with different directions and sunlight conditions are connected to the same circuit, it will have a negative impact on their efficiency. However, some solar inverters have two or more MPPT circuits – solar panels can be grouped and connected together according to their direction, making the entire system more efficient.