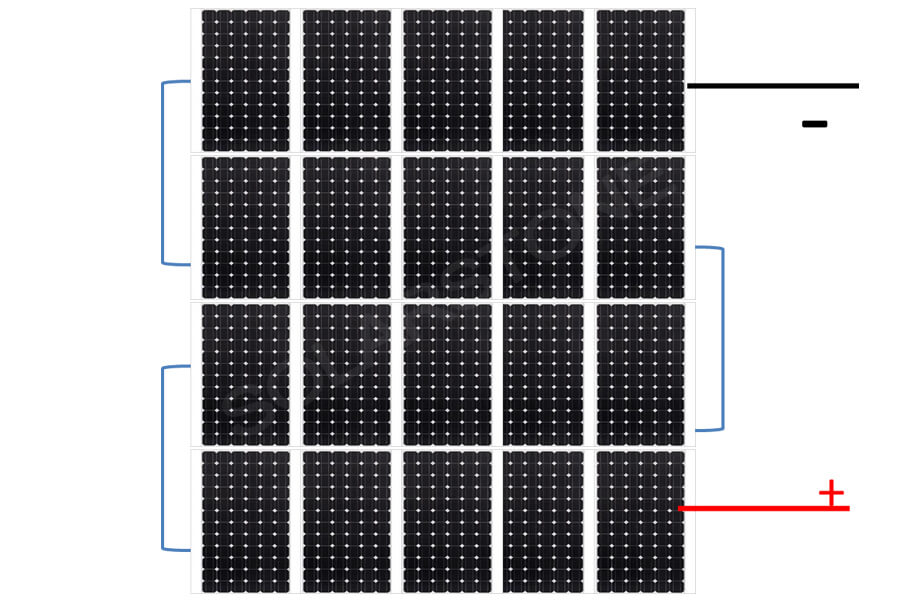
What is the name of the solar panel array?
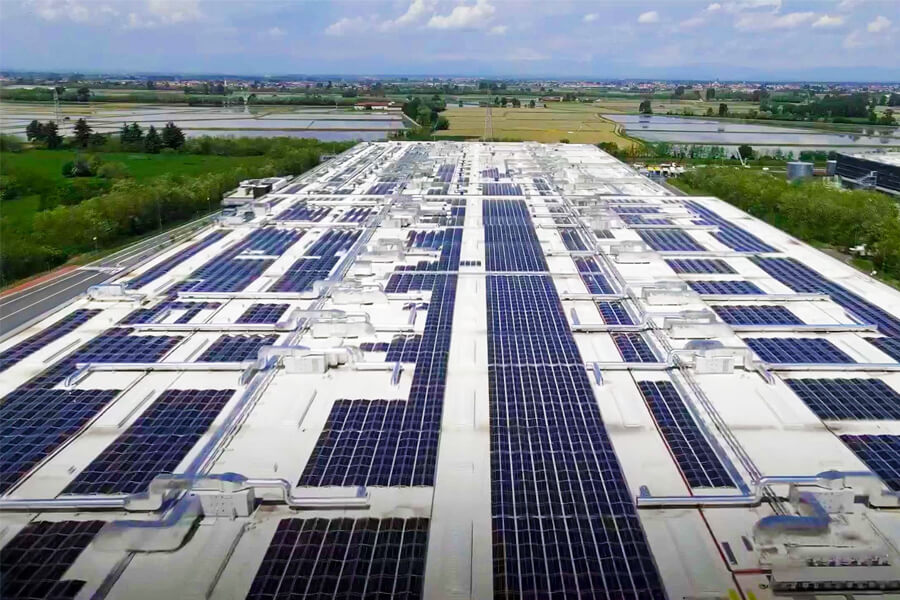
A photovoltaic array is a group of solar panels. A photovoltaic array is a group of solar panels that are connected to form a larger photovoltaic device (PV system), called an array. The larger the overall surface area of the array, the more solar energy it generates.
The solar panel array is the main source of power generation in the complete photovoltaic system. The solar energy generated by a single photovoltaic module or panel is insufficient for general use.
Most solar panel manufacturers provide traditional solar panels with an output voltage of 18V or 36V. PV arrays will provide the required power output by connecting multiple single PV panels in series (for higher voltages) and in parallel (for higher currents).
The flexibility of modular photovoltaic arrays (PV systems) enables designers to develop solar power generation systems that meet a wide range of power needs, regardless of size. Although their power, voltage or current outputs are nominally equivalent, solar panels or modules from different manufacturers should not be mixed in a single array.
This is because the changes in the IV characteristic curve and spectral response of solar cells may cause more mismatch losses within the array, thus reducing its overall efficiency.
Electrical characteristics of photovoltaic
The relationship between the output voltage and current constitutes the electrical characteristics of the solar array. The amount of output current (I) is controlled by the intensity and amount of sunlight (solar irradiance). On the contrary, the operating temperature of the solar cell will affect the output voltage (V) of the photovoltaic array. The manufacturer provides the IV curve of the photovoltaic panel and summarizes the current voltage relationship.
Solar array parameters
VOC=open circuit voltage: This is the highest voltage that the array can provide when nothing is connected to the terminal (open circuit condition). This value is obviously greater than Vmax, which is related to the operation of the photovoltaic array and is determined by the load. The number of photovoltaic panels connected in series determines this number.
ISC=Short circuit current: the maximum current of the photovoltaic array when the output connector is short circuited (short circuit condition). This value is obviously greater than Imax, which refers to the circuit current under normal operation.
Pmax=maximum power point: it refers to the maximum value of the power provided by the array to the load (battery, inverter), Pmax=Imax x Vmax. Watt (W) or peak wattage is the unit of measurement of the peak wattage (Wp) of the solar array.
FF=Fill factor: The fill factor is the relationship between the maximum power that the array can provide under normal operating settings and the results of open circuit voltage and short circuit current (Voc x Isc). The fill factor value indicates the quality of the array. The closer it is to 1, the more power the array can provide. A typical range is 0.7 – 0.8.
Percentage Eff=percentage efficiency: the efficiency of the photovoltaic array is the ratio of the maximum electrical power of the array to the amount of solar radiation it receives. According to the type of cell used (single crystal, polycrystalline, amorphous or thin film), the efficiency of traditional solar cell arrays is generally moderate, ranging from 10% to 12%.
Designers can use the PV IV characteristic curve to build a system whose function is as close to the peak as possible. When receiving the solar radiation corresponding to every 1000W/m2, measure the peak power point of the photovoltaic module.
Create your photovoltaic system
In the design of photovoltaic array and solar power generation system, the received solar radiation and daily energy demand are two decisive parameters. Although shielding any part of the solar array will greatly limit the output of the whole system, the photovoltaic array should match the load requirements and consider any system losses.
If the solar panels are connected in series, the current in each panel will be the same. If the panels are partially shielded, they will not generate the same amount of current. In addition, shaded PV panels will lose power and waste heat instead of generating heat, while bypass diodes will help avoid such problems by providing a backup current path.
Full series systems do not require blocking diodes. However, they should still be used at night or when the solar radiation is low to avoid reverse current from the battery to the array. In addition to sunshine, other climatic factors must be considered.
Because the output voltage of silicon solar cells is related to temperature, designers must understand the current daily temperature, including extreme temperature (low temperature and high temperature) and seasonal fluctuations. In addition, the installation structure must allow for rain and snow. In mountain top installation, wind load is very important.