Solar roofs, solar roads, solar trees, solar toilets… and so on. With the development and innovation of solar, you can see the shadow of solar in all kinds of things. The pace of new things is always moving forward. Now there is a new name, which is about to be known by everyone – solar glass.
What is solar glass?
Crystalline silicon solar cells have poor mechanical strength and are easy to crack. Moisture and corrosive gas in the air will gradually oxidize and corrode the electrodes, which can not withstand the harsh conditions of outdoor work. Therefore, solar cells are usually packaged with solar glass through EVA and back sheet.
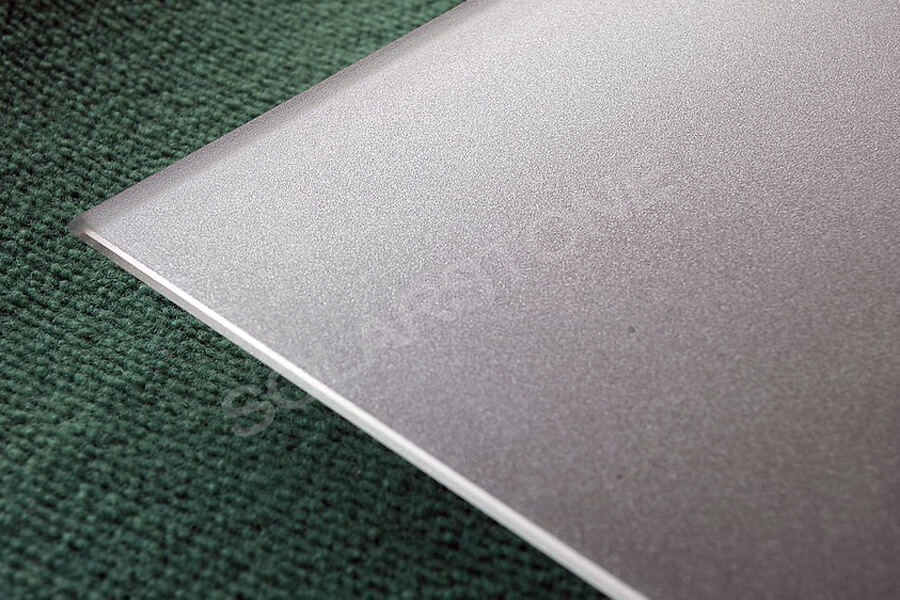
The function of solar glass in solar panels is to protect solar panels from water vapor erosion, block oxygen to prevent oxidation, so that solar panels can withstand high and low temperature, have good insulation and aging resistance. Solar glass is a kind of silicate glass with low iron content, also known as ultra-white embossed glass.
The upper surface of the solar glass is suede, which makes the light directly on the surface of the solar panels not easy to produce a specular reflection. The lower surface is an embossed surface, which can enhance the adhesion with EVA film.
Main materials of solar glass
The main raw materials of solar glass include quartz sand, soda ash, limestone, dolomite, sodium nitrate, mirabilite, sodium pyroantimonate, aluminum hydroxide, etc. Quartz sand mainly plays the role of network forming body, the amount of which usually accounts for more than half of the glass composition.
Soda ash mainly provides sodium oxide and reduces the melting temperature of the glass. The main function of limestone is to adjust the viscosity of glass to a suitable value so that the glass-forming time can meet the forming requirements. The main function of Glauber’s salt is to act as a clarifier to remove the bubbles in the glass and provide the transmittance of the glass.
The production process of solar glass
Solar glass is usually prepared by the calendering method, and the production process can be divided into two stages: original sheet production and deep processing; The original production mainly includes batching, melting, calendering, annealing and cutting;
In the calendering process, the molten glass at about 1100 ℃ is calendered and cooled by calender roller at a certain speed to reach a certain thickness, a certain width, a certain pattern and a 91.5% transmittance glass plate, and then annealed in an annealing furnace, so that the glass plate has a relatively stable stress curve distribution and a certain strength, which is not easy to break and conducive to cutting Processed glass plate.
It should be pointed out that there are differences between the production lines of PV embossed glass and float glass. If the supply of PV glass exceeds the demand, it is impossible to switch directly from the float glass production line.
The deep processing process is usually to coat and toughen the original glass. The purpose of the coating is to improve the light transmittance of photovoltaic glass, and the purpose of toughening is to increase the mechanical properties of glass. The bending strength of toughened glass is 3 ~ 5 times of that of ordinary glass, and the impact strength is 5 ~ 10 times of that of ordinary glass, which improves the strength and safety at the same time.
Performance requirements of solar glass
The solar glass must have good light transmittance. Generally speaking, the light transmittance of uncoated steel sheets (380nm ~ 1100nm wavelength range) is usually more than 91%, while the light transmittance of coated glass after deep processing can reach 93.5%. In addition, solar glass needs to meet certain weather resistance and mechanical properties.
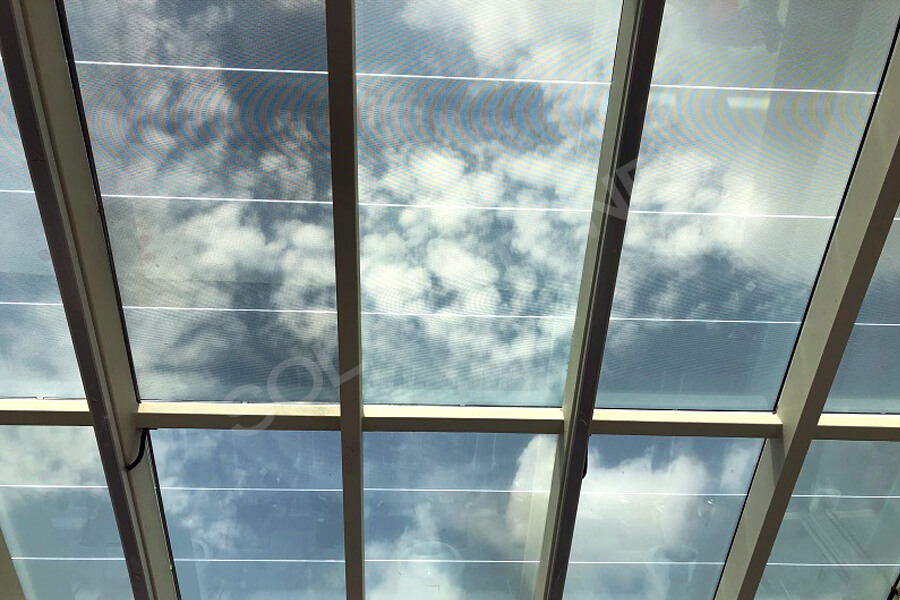
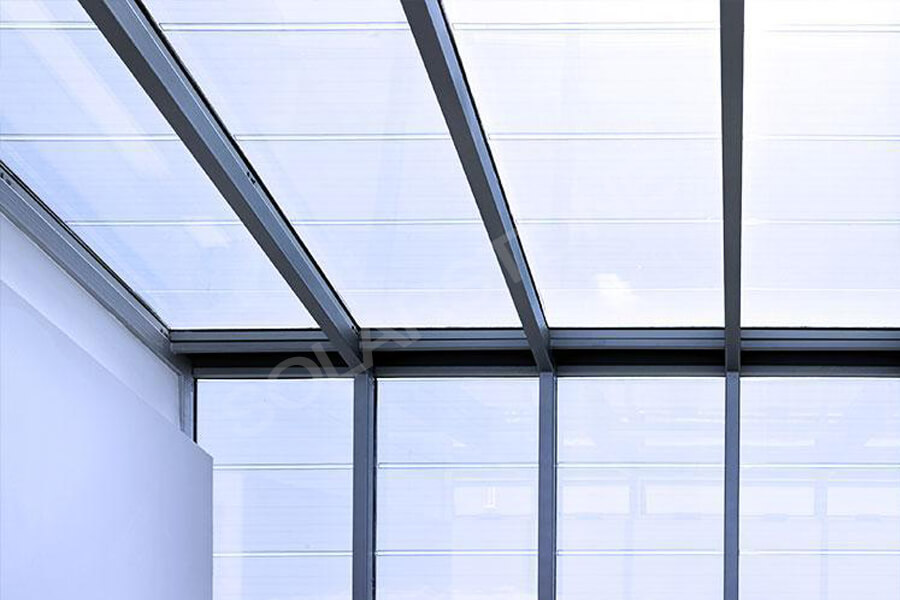
Application of solar glass
It is reported that Germany is the first country in the world to use transparent flat glass as a substrate to develop solar cells. German scientists and technicians installed this kind of plate-shaped solar cell on buildings as window glass, which can directly supply electricity to the residents, and the surplus electricity can also be input into the power grid.
The development and utilization of this kind of glass used for solar cells were soon valued by the United States, Japan and other countries, thus speeding up the development of low-speed rail, high-speed rail, high-speed rail and high-speed rail for solar energy The development and application of ultra-thin glass.