Heterojunctions and traditional crystalline silicon panels
Heterojunction technology improves significant defects such as composite processes on the basis of traditional c-Si panels.
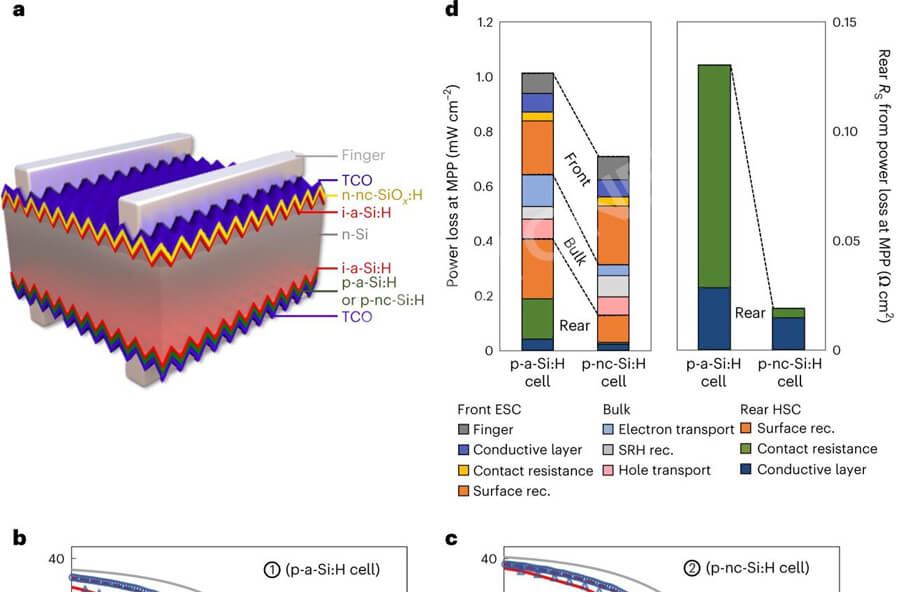
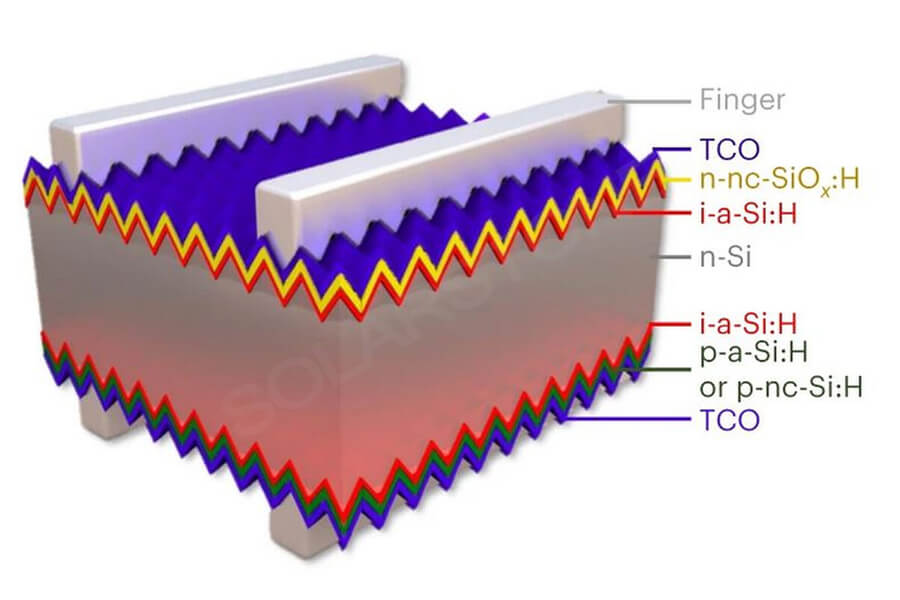
Heterojunction solar panels improve defects in standard c-Si modules and reduce surface recombination. This technology has higher recording efficiency and improves the lifespan of modules. Due to these improvements, the HJT panel has a lower temperature coefficient, resulting in better performance at different extreme temperatures.
Heterojunction technology was first developed in the early 1990s, but it has only become popular in recent decades, which explains a 5% market share and high production costs. However, this is only a temporary setback and is expected to be surpassed in the near future.
Heterojunctions and double-sided panels
The structure of double-sided solar panels is similar to that of heterojunction solar panels. Both include passivation coatings, which can reduce surface recombination and improve efficiency.
HJT technology has a high recording efficiency of 26.7%, but the double-sided efficiency exceeds 30%. Strangely, the double-sided photovoltaic modules used to achieve this efficiency combine HJT technology with double-sided and other technologies.
HJT batteries can be designed for single-sided or double-sided use, reducing the reason for comparing them to each other as they can be combined to produce excellent double-sided HJT solar panels. The main difference is that double-sided technology can use other fundamental techniques that are different from heterojunction technology.
Summary: What are the benefits of heterojunction panels?
Heterojunction solar panels may be very beneficial because they have improved technology and enormous potential in the solar energy industry. These are some of the main benefits of this technology.
High efficiency
The conversion efficiency of single-sided modules is 26.07%, while that of double-sided modules exceeds 30%. Heterojunction has become one of the most efficient solar technologies in the industry. This makes applications in areas with limited space and requiring large power generation capacity more convenient.
Good temperature coefficient
Heterojunction solar cell technology is less affected by temperature changes. This makes it very suitable for high-temperature applications, which can have a negative impact on the performance of standard c-Si modules.
High double-sided performance
Heterojunction batteries have a high double-sided coefficient of 92%, which makes heterojunctions exhibit excellent performance when designed as double-sided components. This technology is becoming increasingly popular in utility scale applications seeking to utilize albedo resources.
Simple manufacturing process
Heterojunction solar cells have additional steps in the manufacturing process, but this will not significantly increase costs. This technology only involves 5-7 steps in the manufacturing process, and the price of the required equipment continues to decrease, demonstrating HJT’s great hope for the future.
Typical Applications of Heterojunction Solar Energy Technology
Heterojunction solar panels have a wide range of applications, opening the way for the solar energy industry to further increase solar energy applications. These are some of the most common applications of this technology.
(1) Limited space applications (solar tiles and BIPV)
The high conversion efficiency of HJT makes it very suitable for limited space applications. The two popular applications are the manufacturing of solar tiles and integrated photovoltaic building (BIPV) products. Tesla roof is one of the most popular roof panels using this technology, which greatly improves the solar energy efficiency of photovoltaic homes.
(2) Power supply for wearable devices
Reducing the size of wafer based layers can pave the way for the integration of HJT technology with wearable devices. This will provide power for the device to expand its autonomy during the day.
(3) Application of Public Utility Scale
Conventional single-sided heterojunction solar panels can be used for utility scale applications, especially suitable for double-sided heterojunction solar panels. This will result in an average efficiency of over 30% for solar power plants, which can not only utilize direct sunlight but also utilize albedo resources.
Outlook on the Future of Heterojunction Technology
Heterojunction is a promising technology with high recording efficiency. This technology paves the way for the solar energy industry to improve the efficiency of daily photovoltaic modules and reduce the levelized energy cost (LCOE) of solar power generation.
A major limiting factor of heterojunction technology is the current manufacturing process and material costs. With the development of technology and research on other materials, this may no longer be a promise in the future, but it can also improve the efficiency of heterojunction solar panels and reduce costs.