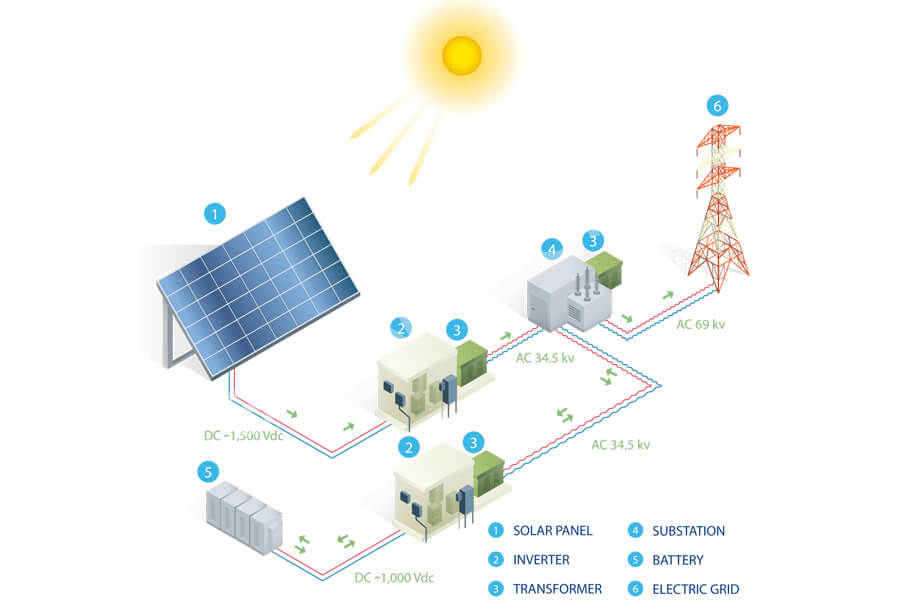
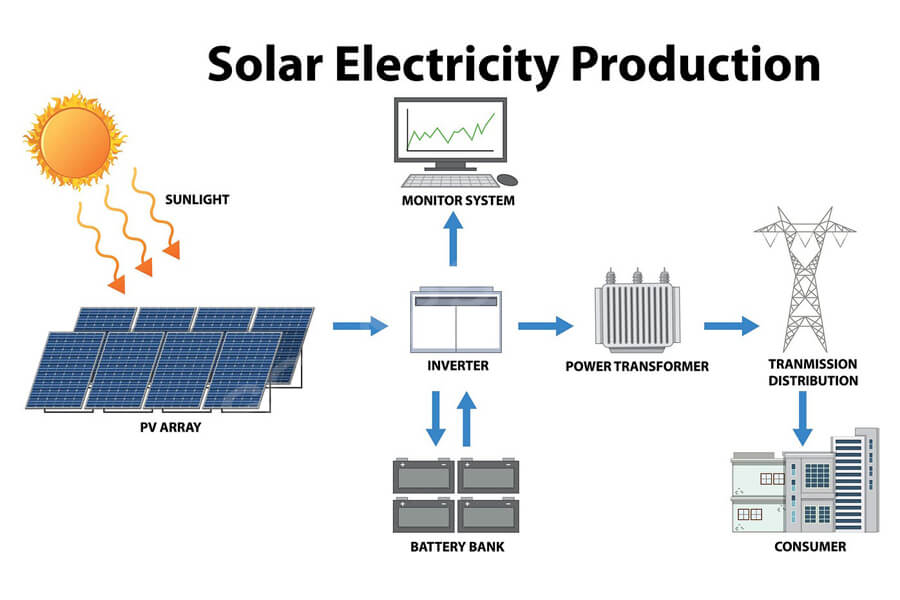
To understand the photovoltaic industry, it is necessary to first understand the core raw materials of photovoltaics.
Silicon material is the core raw material of photovoltaic power generation systems. Photovoltaic silicon material, also known as solar grade polycrystalline silicon (SoG Si), is the upstream raw material in the photovoltaic industry chain.
It is a gray black solid with metallic luster, with high melting point (1410 ℃), high hardness, brittleness, and inactive chemical properties at room temperature. It also has semiconductive properties and is an extremely important excellent semiconductor material, known as the “black gold” in the photovoltaic industry chain.
Secondly, it is important to understand that the photovoltaic industry is focused on generating electricity – photovoltaic power generation
Photovoltaic power generation is a technology that utilizes the photovoltaic effect at semiconductor interfaces to directly convert light energy into electrical energy.
It mainly consists of three parts: solar panels (components), controllers, and inverters, with the main components composed of electronic components. After being connected in series and packaged for protection, solar cells can form large-area solar cell modules, which are combined with power controllers and other components to form photovoltaic power generation devices.
Photovoltaic power stations are mainly divided into two categories based on their scale and functions: centralized and distributed.
The installation of photovoltaic power stations has higher flexibility compared to wind power. It can not only be installed on a large scale, but also distributed in multiple scenarios such as building surfaces and outdoor environments.
Centralized photovoltaic power station: Simply put, it is a power station specialized in generating and selling electricity, occupying a very large area and having high costs. To be more specific, it refers to installing photovoltaic arrays in wider areas such as mountains, water surfaces, and deserts.
After being exposed to sunlight, the photovoltaic array can generate direct current, which is then converted into alternating current by an inverter and connected to the power grid through a booster station. The scale of centralized photovoltaic power stations is generally large, generally above 10MW, and currently there is an increasing number of super large photovoltaic power stations above 100MW.
Distributed photovoltaic power station: Simply put, the electricity generated by the power station can be sold on one hand, and can also be used by oneself on the other hand, with a small footprint and low cost.
To be more specific, it refers to the construction of photovoltaic power generation facilities near the user’s site, with the operation mode mainly based on the user’s spontaneous self use, excess electricity connected to the grid, and characterized by balanced adjustment in the distribution system.
Distributed photovoltaic power generation follows the principles of adapting to local conditions, clean and efficient, decentralized layout, and nearby utilization, fully utilizing local solar energy resources to replace and reduce fossil energy consumption.
If divided by business models, there are mainly mountain light, ground light, fishing light, and agricultural light.
Mountain light is the installation of photovoltaic power stations in mountainous areas; Ground light refers to the installation of photovoltaic power stations on equal levels in the northwest Gobi region; Fishing light generates electricity while raising fish; Similarly, agricultural light generates electricity while planting or grazing.
Three modes of photovoltaic power generation
01 All spontaneous self use
Simply put, it means that the user’s photovoltaic system generates electricity for their own use and consumption. Commonly used for off grid systems.
02 Spontaneous self use, surplus electricity connected to the grid
The user’s photovoltaic system generates electricity for their own use first, and the excess electricity is sold to the grid. This mode is currently the most widely accepted and widely used among users, and it is also the main mode promoted by various regions.
03 All internet access
All the electricity generated by the user’s photovoltaic system is sold to the power grid. This mode was more common earlier, but now it is gradually decreasing
Two types of benefits from photovoltaic power generation
01 Electricity revenue
Photovoltaic system power generation can save a certain amount of electricity bills every month, which means income from other perspectives.
02 Electricity sales revenue
The excess electricity used by users can be sold to the country, and the selling price will be based on the benchmark electricity price of local coal-fired desulfurization units.